You Won’t Believe What Apple and Google Just Banned in the App Stores

As of July 2025, Apple and Google have intensified their efforts to regulate the content available on their app stores, responding to global concerns over data privacy, national security, and user protection. Several high-profile apps have been removed, reflecting a growing trend of stricter app store governance.
1. DeepSeek Faces Removal in Germany Over Data Privacy Concerns
Germany’s data protection commissioner has requested that Apple and Google remove the Chinese AI startup DeepSeek from their app stores due to concerns over unlawful data transfers and privacy violations. DeepSeek has been accused of transferring German users’ personal data to China without ensuring protection levels equivalent to EU standards.
Despite a prior request in May for DeepSeek to comply with EU data transfer requirements or withdraw voluntarily, the company did not respond. DeepSeek’s privacy policy indicates that user data—including AI interaction requests and uploaded files—is stored on servers in China, raising further national security concerns. Apple and Google have yet to respond to the request.
2. TikTok and Other ByteDance Apps Temporarily Removed in the U.S.
In January 2025, Apple and Google removed TikTok and several other apps developed by ByteDance from their U.S. app stores following a Supreme Court decision upholding a law aimed at restricting foreign-controlled applications. The move came into effect on January 19, 2025, as part of compliance with the Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act. Affected apps included TikTok, CapCut, Lemon8, and others.
These apps were no longer available for download or updates in the U.S., and in-app purchases were disabled for affected users. However, on February 13, 2025, TikTok was restored to the Apple App Store and Google Play Store after the Justice Department informed Apple and other major tech companies that they would not be fined for bringing the app back for download.

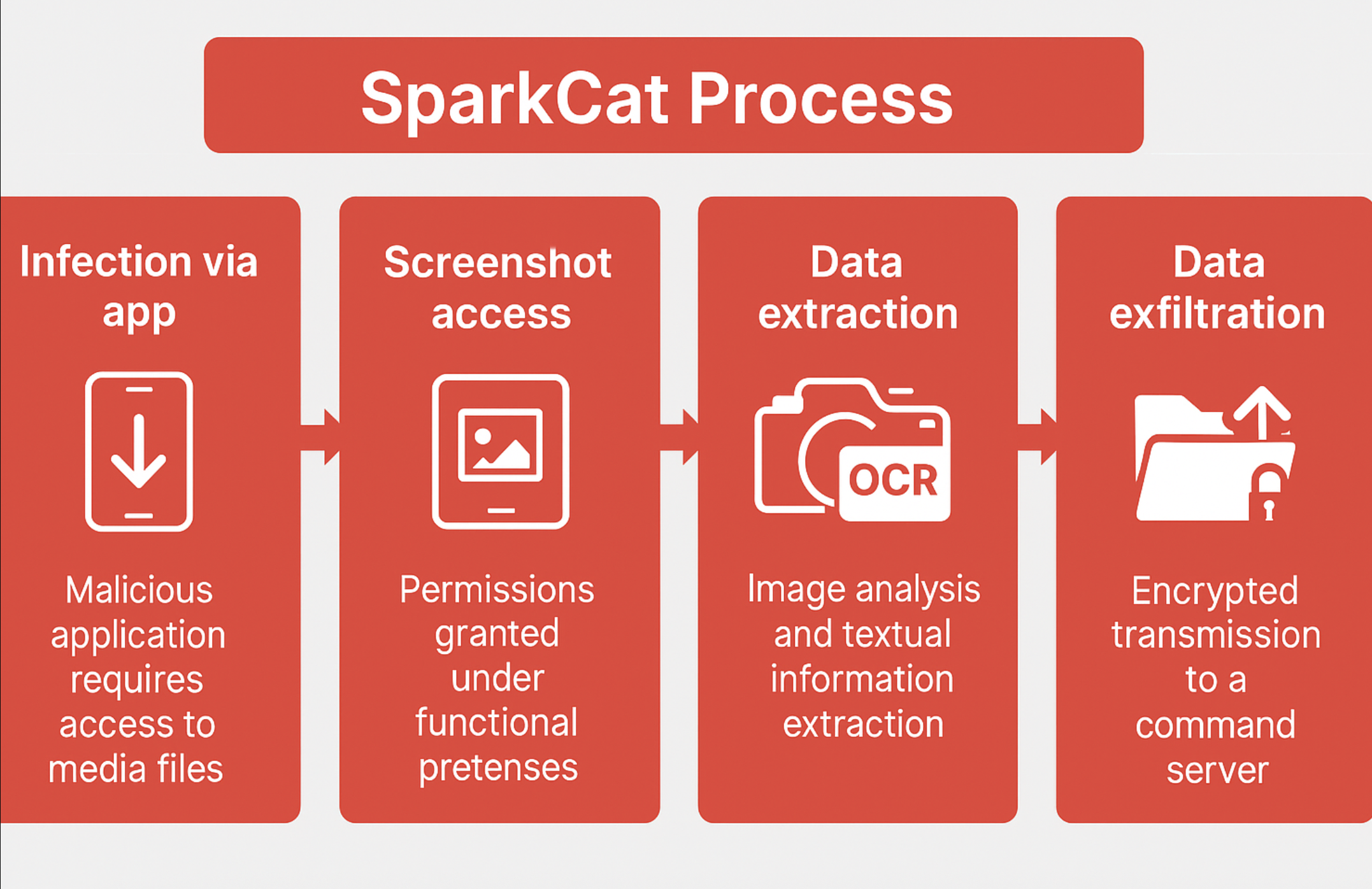
3. Malicious Apps Containing ‘SparkCat’ Malware Removed
In early 2025, Apple and Google pulled as many as 20 apps from their respective app stores after security researchers found the apps were carrying data-stealing malware known as ‘SparkCat’. The malware had been active since March 2024 and was initially found within a food delivery app used in the United Arab Emirates and Indonesia.
Researchers later discovered the malware on 19 other unrelated apps, which were cumulatively downloaded more than 242,000 times through Google’s Play Store. The malware was designed to capture text visible on the user’s display, scanning image galleries for keywords to find recovery phrases for cryptocurrency wallets across various languages. Upon receiving the report from the researchers, Apple and Google removed the compromised apps from their stores.
4. Apple Revises App Store Policies in the EU to Avoid Fines
Apple has revised its App Store policies in the European Union in an effort to comply with the Digital Markets Act (DMA) and avoid further financial penalties. Following an April ruling by the European Commission that deemed Apple’s terms restrictive and a breach of the DMA, the tech giant was fined €500 million ($583 million) and given a 60-day deadline to change its practices or risk additional daily fines of up to 5% of global turnover.
In response, Apple is now allowing developers more freedom to direct users to external purchasing options and has introduced a new tiered services fee model for such transactions. Although Apple maintains it disagrees with the Commission’s ruling and plans to appeal by July 7, it aims to avoid further sanctions by adjusting its policies.

What This Means for Users
These developments highlight the increasing scrutiny and regulatory actions tech giants face globally. For users, this means:
- Enhanced Data Privacy: Apps that do not comply with data protection standards are being removed, ensuring better privacy for users.
- App Availability Fluctuations: Popular apps may become temporarily unavailable due to regulatory actions, affecting user access.
- Increased Transparency: Revised policies aim to provide users with more information and control over their data and app interactions.
As the digital landscape evolves, staying informed about these changes is crucial for users to navigate app availability and data privacy concerns effectively.